physics
Learn from yesterday, live for today, hope for tomorrow. The important thing is to not stop questioning.” ― Albert Einstein
Energy
Energy means invisible strength of doing work. Energy is a measure of
how much work we can do. Energy needed to do certain work will always
remain the same.
For example energy required to lift 500lits. of water
to height of 10m. will always remain the same irrespective of doing it
manually or by using engine. We can only do the work faster by using
engine.
Common unit of energy is the kilowatt-hour (kWh). 1 KWh energy means, one kW of power will last one hour.
There are three Main types of Energy:-
1) Kinetic Energy


W = F*d Kinetic Energy
= K.E.
= 1/2 mv^2 Joule (J) is the standard unit of Kinetic Energy




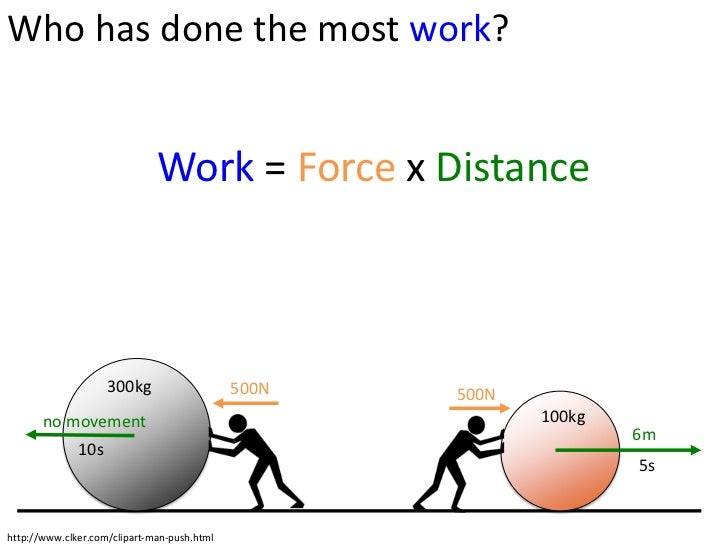
Kinetic Energy– is simply the energy in motion.An energy possessed by a body because of its motion. If a body has energy, then it is capable of doing work. Energy has the capability of doing work on our body. Work = Force x distance
W = F*d Kinetic Energy
= K.E.
= 1/2 mv^2 Joule (J) is the standard unit of Kinetic Energy


2) Potential Energy
(Gravitational)

Mechanical Energy Theorem (Conservation of Mechanical Energy)
M.E = K.E + P.E

Conservation of Energy– The initial total of Mechanical Energy can be found and the Potential Energy decreases as Kinetic Energy (and speed) increases. In systems with non conservative forces, total M.E is changed. If friction is the non conservative force, then the total M.E is lost.
Potential Energy – the energy possessed by a body. It is also define as a stored energy. Either by virtue of its position or configuration.Gravitational Potential Energy = mgh P.E. = mgh Joule (J) is its standard unit. Elastic Potential Energy = 1/2kx^2 P.E. = 1/2kx^2 Newton meter (N/m) as its standard unit.1 N.m = 1 J

Mechanical Energy Theorem (Conservation of Mechanical Energy)
M.E = K.E + P.E

Conservation of Energy– The initial total of Mechanical Energy can be found and the Potential Energy decreases as Kinetic Energy (and speed) increases. In systems with non conservative forces, total M.E is changed. If friction is the non conservative force, then the total M.E is lost.
3) Chemical Energy



Electrical, Heat, sound, solar, wind etc. are other examples of different forms of energy. Many times energy is invisible. It is visible by their effects.
Kerosene, diesel, food, wood contains energy in the
form of chemical energy. When these things burn energy comes out in the
form of heat energy.
Stone falling from height (or anything in motion) contains
energy. The object placed at highest place also contains hidden energy.
This is called potential energy.
An object in motion contains kinetic
energy.
Law of Energy Conservation
Energy can neither be created nor can be destroyed. Only one form of
energy can be converted to other form of energy. Energy is immortal. It
is not distortable.
Energy Conversion
- We eat food. Food contains chemical energy, in it after digestion this chemical energy is kept in the chemical form in our body and as and when required it gets burnt and gets converted into other forms of energy
- When we fetch the water from the well, the energy in the form of chemicals in our body gets converted into potential energy of water. Water will contains energy equal to the amount of work done while lifting the water.
- If we pour the water on the land, where the energy in it will go? If this water gets percolated in land then as it will go deep into the earth, potential energy in it will get converted into heat through friction. We never felt the heat since land is big and quantity of heat generated is comparatively smaller.
- When we do cycling, chemical energy from food gets converted into kinetic energy. Once cycle catches the speed then we can move with same speed without peddling. At this time our body and cycle has kinetic energy in it. When we want to get down from the cycle, we reduce the speed by pressing the breaks. Kinetic energy gets converted into heat energy by friction and the ream of the cycle becomes hot.
- Whenever we change the form of energy, some amount of energy gets wasted in the form of heat. Our objective is to convert maximum amount of energy in the desired form for use. This is called as efficiency.
In diesel engine, when we burn diesel approximately 40% of energy
gets converted into kinetic energy of water. When water is lifted to
desire height, kinetic energy gets converted into potential energy.
Remaining 60% of energy is wasted in the form of heat. This means the
efficiency of diesel engine is 40%.
In the past, relation between energy and work done was not clearly
understood. Therefore, units of measurement of heat and work were
different. Heat was measured in terms of calories and unit of work in
terms of joule. These two units are still in use because it’s easier to
calculate heat in calories and work in joule.
We can convert calories
into joule by using formula 1calorie = 4.2 joule. Power is the rate of work done or rate of energy consumed. It tells us
amount of joules used or required in one second.
If one-joule energy is
used in one second, then it is said that one-watt power is used.
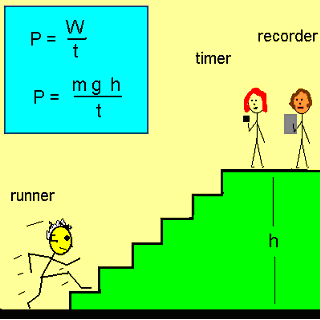
Power (unit W watt) = J/S joule/second
= Energy used (in joule) / time taken